Table of Contents
In an era of profound changes driven by digitalization and global interconnectedness, our working world is fundamentally transforming. The concept of "New Work" is gaining increasing importance - but what lies behind it and what competencies do we need to be successful in this new world of work?
What is New Work?
The term "New Work" goes back to philosopher Frithjof Bergmann, who developed a vision of work based on autonomy, freedom, and personal development in the 1980s. Today, New Work encompasses various aspects of modern work design:
- Working time flexibility: Part-time, flextime, trust-based working hours, job sharing
- Workplace flexibility: Home office, remote work, coworking
- Collaborative digital work: Networked working, interdisciplinary projects
- New organizational structures: Flatter hierarchies, self-organization
The COVID-19 pandemic has massively accelerated this transformation. According to a Bitkom study, 84% of surveyed companies stated that digitalization has gained importance due to the pandemic.[1] It also became apparent that companies with already digitalized business models and processes weathered the crisis better.
The "New Work Switzerland" whitepaper [2] defines New Work as creating an attractive work environment under conditions of rapid technological change and skilled labor shortages to attract and retain talent. The focus is on employee satisfaction, because new is not inherently better. There are no universal solutions; each organization must find its own path to being a good and sustainable employer.
The Three Key Drivers of New Work
- Digital Transformation: It is revolutionizing work models by promoting flexibility, collaboration, and innovation. Mobile internet and cloud computing enable time and location-independent work, creating space for creativity and personal responsibility. Digital competencies, lifelong learning, and self-leadership are becoming focal points.
- Hybrid Work: It has established itself as a central element of New Work and combines the advantages of office work and remote work. This increases flexibility and reduces commuting time. Employees can choose their work environment according to their tasks and preferences, which largely promotes satisfaction.
- The competition for Talent: The shortage of skilled workers is a concern for many organizations. Flexible work models are a decisive advantage in the competition for skilled professionals. They also expect appropriate compensation, meaningful tasks, transparent communication, and a trust-based corporate culture.
Eight Key Action Areas of New Work
To implement New Work in concrete terms, eight key action areas can be identified for organizations [3]:
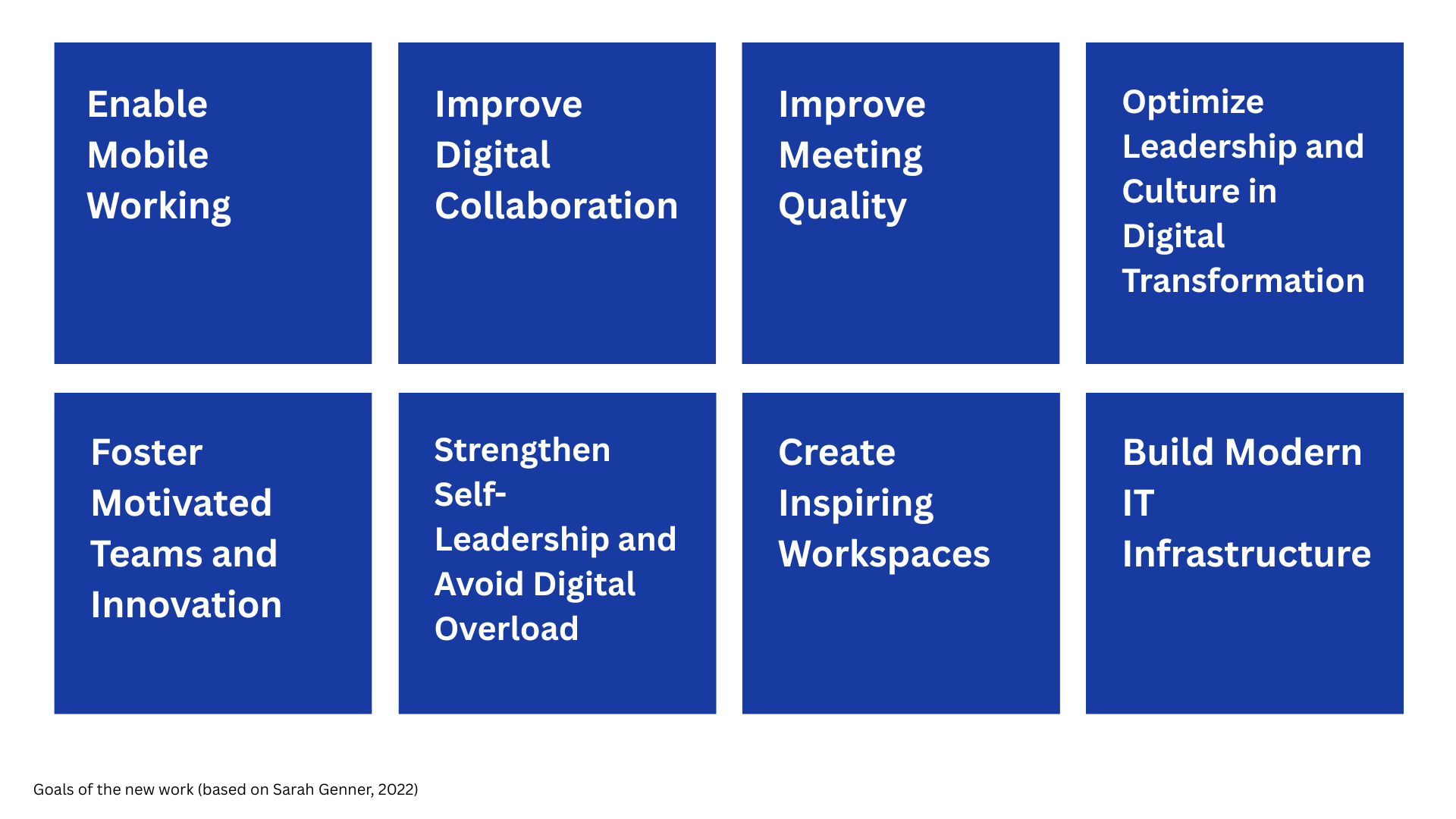
1. Enable Mobile Working
The flexibility of work location is a core aspect of New Work. Mobile working means more than just "working from home" - it's about the fundamental freedom to work wherever one can be productive. This requires:
- Cloud-based systems and mobile devices
- Clear agreements regarding expectations about presence and availability
- Special support for onboarding new employees
- Fair balance between employees in mobile and location-bound jobs
Studies show that when well implemented, mobile working can increase both productivity and employee satisfaction. The majority of employees prefer two to three days of home office per week.
2. Improve Digital Collaboration
Successful digital collaboration is based not only on the right tools but also on established processes and communication rules:
- Use of diverse collaboration tools
- Clear agreements about how to work together
- Promotion of asynchronous working methods for more flexibility
- Training employees in the productive use of digital tools
Important to understand: Just because documents are shared doesn't automatically mean there's a shared understanding (co-creation).
3. Improve Meeting Quality
Meetings - whether virtual or in person - are often inefficient and time-consuming. Improving meeting culture is therefore an important component of New Work:
- Conscious decision about the format: in-person, online, or hybrid
- Consistent evaluation of the necessity of each meeting
- Clear agenda and objectives for all meetings
- Shortened standard times (e.g., 25 or 45 minutes instead of 30 or 60)
- Introduction of meeting-free times for focused work
4. Optimize Leadership and Culture in Digital Transformation
The success of New Work depends significantly on an adapted leadership and corporate culture:
- Fostering identification with the job, team, and organization
- Development of a contemporary understanding of leadership (from controller to coach)
- Building psychological safety as a foundation for innovation
- Establishing a feedback and learning culture
- Strengthening organizational culture through shared purpose and clear goals
"Anyone who reduces digitalization to technologies is wrong. It requires adapting corporate culture, new business models, and process adjustment." The type of tool always changes our way of thinking and acting.
5. Foster Motivated Teams and Innovation
Intrinsic motivation is the fuel for innovation and engagement. New Work aims to strengthen this:
- Trust and psychological safety as central factors
- Creation of autonomy and room for creativity
- Connecting individual work with a greater sense of purpose
- Promotion of continuous learning
- Implementation of agile methods to foster creativity
6. Strengthen Self-Leadership and Avoid Digital Overload
In more flexible work structures, self-leadership becomes a key competency:
- Development of skills in self-organization, structuring, and motivation
- Promotion of digital wellbeing and conscious breaks
- Awareness in occupational health management
- Support in developing individual strategies for boundary management
Digital overload can have serious consequences: According to studies, 36% of respondents report negative effects of permanent digital accessibility on their productivity and 40% on their health. [4]
7. Create Inspiring Workspaces
Even in times of remote work, the office remains an important place - albeit with a changed function:
- Transformation of the office from a pure workplace to a meeting and collaboration space
- Provision of meeting rooms, workshop zones, and gathering areas
- Functional and human-friendly furnishing
- Consideration of different needs (fixed desks vs. flex desks)
- Attention to ergonomic requirements
8. Build Modern IT Infrastructure
A powerful, user-friendly IT infrastructure forms the technical foundation for New Work:
- Modern technological equipment to motivate employees
- Balance between system administration/cybersecurity and individual preferences
- Cloud solutions for mobile working
- Professional backup strategies as protection against cyber attacks
However, the productivity paradox of IT shows: Technology alone is not enough - what's crucial is the meaningful integration into processes and culture.
The Importance of Trust-Based Leadership and Psychological Safety
A central aspect of successful teams in the new world of work is the concept of psychological safety. According to researcher Amy Edmondson, psychological safety is "a shared belief that it's okay to take risks, express opinions, ask questions, and admit mistakes - without having to fear negative consequences."
Google's "Aristotle" project [5] identified psychological safety as the most important factor for successful teams. The study showed that teams with high psychological safety:
- Are 76% more engaged and productive
- Work 50% more innovatively
- Have 50% lower turnover
New Work is at its core a culture and mindset issue. Any exciting new initiative will fail if it cannot be anchored in the culture. To promote new ways of working and openness to innovation, trust-based leadership and culture are needed.
The Great Place To Work® European Workforce Study 2025 [6] emphasizes: Hybrid work is becoming the norm. When employees can decide, 57 percent prefer hybrid work forms over on-site work. Successful workplace flexibility is a product of high-trust leadership. Hybrid workers are less likely to leave the company, and hybrid work leads to higher economic success.
Key Competencies for New Work
What does it take to succeed in this new world of work? The following key competencies are crucial:
1. Digital Competencies
- Digital Literacy: Basic understanding of digital media and systems
- Information Competency: The ability to search for, filter, and process digital information
- Data Protection Awareness: Responsible handling of one's digital identity
- Collaboration Tools: Competency in using digital collaboration tools
2. Self-Competencies
- Self-Leadership: The ability to lead and motivate oneself
- Boundary Management: Active management of work-life boundaries
- Resilience: Resistance to stress and changes
- Learning Ability: Continuous development through lifelong learning
- Flexibility: Openness to new things and willingness to adapt
3. Social Competencies
- Team Skills: Successful collaboration in mixed teams
- Communication Skills: Clear and constructive communication, including in digital channels
- Empathy: Understanding other perspectives and needs
- Conflict Management: Constructive handling of disagreements
- Networking Ability: Building and maintaining relationships, including in hybrid work settings
4. Methodological Competencies
- Critical Thinking: The ability to question and evaluate information
- Analytical Thinking: Recognizing and structuring complex relationships
- Problem-Solving Competency: Identifying challenges and developing solution strategies
- Project Management: Structured planning and execution of projects
- Agile Work Methods: Familiarity with flexible work methods like Scrum or Kanban
5. Leadership Competencies
- Digital Leadership: Leadership in digital and hybrid work environments
- Change Management: Guiding transformation processes
- Agile Leadership: Setting direction while leaving the path to the team
- Coaching Skills: Supporting and developing employees
- Ambiguity Tolerance: Dealing with uncertainty and complexity
Conclusion: New Work as Continuous Development
New Work is not a fixed state but a continuous development process that encompasses both technological and cultural aspects. It's not about adopting every new work form or digital tool without reflection. Rather, we should critically question which elements make sense for our specific situation and offer real added value.
As Jürg Stuker emphasizes in the CAS New Work: "New is not inherently better." It's about consciously designing what works best for your own organization and employees. This requires continuous reflection and adjustment - both at individual and organizational levels.
In my work, I experience daily the profound changes that the working world demands of us: How do we design digital processes meaningfully? How can we establish a flatter hierarchy in a team, and what does leadership mean in the context of New Work? Those who begin to integrate the principles of New Work quickly recognize: Openness, willingness to learn, and the ability for self-reflection are required from all of us. Because at its core, New Work is about making the working world more human and creating space for development, meaning, and self-determination - in the midst of a constantly changing, unstable world. Or as Martin Oswald aptly puts it: "At its core, it's always about people. We can only succeed if we manage to take employees along on this journey."
Are you interested in the topic of New Work and want to delve deeper? Then I can warmly recommend the CAS New Work at HWZ.*
[2]: https://sarah.genner.cc/blog/whitepaper-new-work-schweiz
[3]: sarah.genner.cc/blog/was-bedeutet-new-work-konkret
[4]: https://digitalcollection.zhaw.ch/items/55d13f1b-c421-4fd2-af81-c01986674503
[5]: https://rework.withgoogle.com/en/guides/understanding-team-effectiveness#introduction
[6]: https://europeanworkforcestudy.com
- If you register for a course at HWZ, I would appreciate if you mention that it was based on my recommendation. I will then receive a small thank you from HWZ (Digital Friend Referral Program: https://hwzdigital.ch/friend-referral-share-your-love-for-hwz-digital/).

